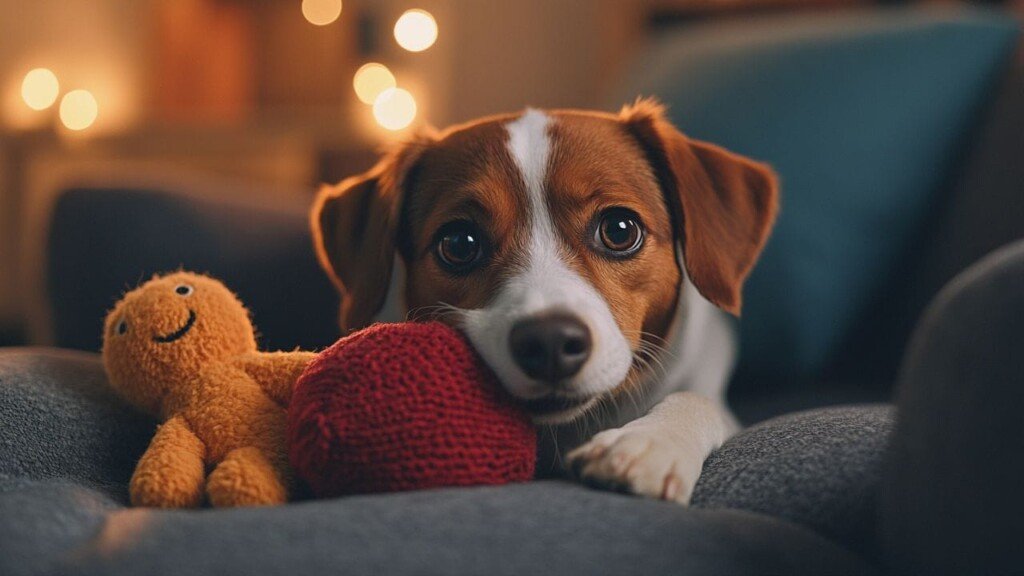
We’ve all seen it: a dog with an unwavering attachment to a particular toy, often tattered and well-worn.
This seemingly adorable behavior is more than just a quirky pet trait; it’s rooted in fascinating canine psychology.
Understanding the science behind this obsession can deepen our appreciation for our furry friends’ complex emotional lives.
The Comfort of Familiarity
Dogs, like humans, find comfort in familiar objects, especially those associated with positive experiences.
A favorite toy often becomes a source of security, much like a child’s beloved stuffed animal.
This attachment is particularly evident during times of stress or when the dog is in unfamiliar environments.
Scent as a Powerful Memory Trigger
A dog’s sense of smell is incredibly powerful and plays a crucial role in their toy preferences.
As a toy accumulates the dog’s scent, it becomes increasingly familiar and comforting.
This scent association can make an old, worn toy far more appealing than a brand new one.
Want to keep up to date with new animal stories?
The Role of Texture and Mouthfeel
The specific texture of a toy can be deeply satisfying to a dog, triggering positive sensory experiences.
Some dogs may prefer soft, plush toys that mimic prey, while others might favor harder textures for chewing.
This preference often relates to the dog’s breed-specific instincts and individual personality.
Positive Reinforcement and Learned Behavior
Dogs quickly learn to associate specific toys with enjoyable activities like play or training sessions.
Repeated positive experiences with a particular toy can strengthen the dog’s attachment to it.
This learned behavior is a form of classical conditioning, similar to Pavlov’s famous experiments.
The Evolutionary Aspect: Prey Drive
Many dogs’ obsession with certain toys can be linked to their innate prey drive.
Toys that squeak or have certain movements may trigger a dog’s hunting instincts.
This explains why some dogs seem particularly attached to toys that they can “hunt” or “kill” through play.
Emotional Bonding and Toy Preference
Dogs often favor toys that are associated with their human companions.
A toy that’s frequently used in interactive play with the owner can become especially prized.
This preference reflects the strong emotional bond between dogs and their human families.
The Science of Novelty vs. Familiarity
While dogs can become obsessed with one toy, they also benefit from novelty in their playthings.
Research shows that dogs, like humans, experience a spike in dopamine when presented with new stimuli.
Balancing familiar favorites with new toys can provide optimal mental stimulation for your pet.
Stress Relief and Coping Mechanisms
A favorite toy can serve as a coping mechanism for dogs experiencing anxiety or stress.
The act of chewing or carrying a beloved toy can release endorphins, promoting a sense of calm.
This self-soothing behavior is similar to human stress-relief techniques like squeezing a stress ball.

The Impact of Early Experiences
A dog’s attachment to a specific type of toy can sometimes be traced back to early life experiences.
Puppies exposed to certain toys during critical developmental periods may form lasting preferences.
This phenomenon underscores the importance of diverse, positive experiences during a dog’s formative weeks.
Individual Personality and Toy Preferences
Just as humans have unique personalities, dogs too have individual traits that influence their toy preferences.
Some dogs may be more possessive of their toys, while others are happy to share.
These variations in behavior reflect the complex interplay of genetics, environment, and individual experiences.
The Role of Breed-Specific Behaviors
Certain breeds may be more prone to toy obsession due to their historical working roles.
For instance, retriever breeds might show a stronger attachment to ball-like toys.
Understanding breed-specific tendencies can help in selecting appropriate toys for your dog.

Cognitive Benefits of Toy Attachment
A dog’s obsession with a toy can actually provide cognitive benefits.
Engaging with a favorite toy stimulates problem-solving skills and maintains mental acuity.
This mental exercise is particularly beneficial for aging dogs, potentially slowing cognitive decline.
Conclusion: Embracing Your Dog’s Unique Attachments
Your dog’s devotion to that one special toy is a window into their rich emotional and cognitive world.
Far from being just a cute quirk, this behavior is grounded in complex psychological and evolutionary factors.
By understanding and appreciating this aspect of canine behavior, we can forge even deeper bonds with our four-legged companions.
Share this post to shed light on the fascinating science behind your dog’s favorite toy! Have you noticed your furry friend’s unwavering devotion to a particular plaything? Now you know it’s not just adorable – it’s a reflection of their complex emotional and cognitive processes.
SHARE now with your friends!